Currently Empty: $0.00
Understanding the distinction between structured and unstructured data is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage their data effectively. In this article, we’ll delve into the definitions of structured and unstructured data, explore their differences, and highlight their significance in the realm of data analytics and business intelligence.
What is Structured Data?
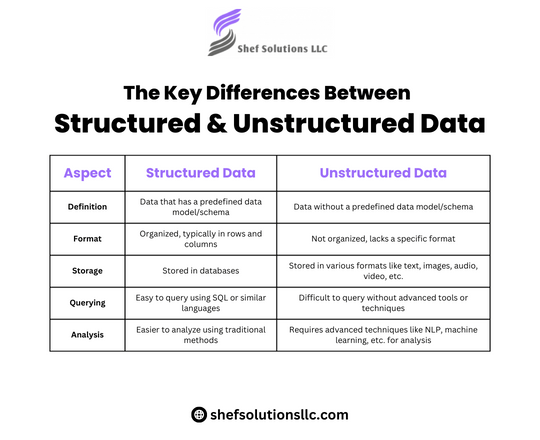
Structured data refers to information that is organized in a highly predictable and pre-defined manner. It typically resides in relational databases or spreadsheets and is represented in tabular form with rows and columns. Each data element is assigned a specific data type and is organized into categories such as dates, numbers, or text.
Examples of structured data include customer information (name, age, address), transaction records, and inventory lists.
What is Unstructured Data?
On the other hand, unstructured data lacks a predefined data model and does not fit neatly into traditional databases. It encompasses a wide variety of data types and formats, including text documents, images, videos, social media posts, emails, and sensor data.
Unstructured data is often characterized by its complexity, variability, and sheer volume. Unlike structured data, it does not adhere to a rigid schema, making it more challenging to analyze using traditional database management techniques.
What is the main difference between structured and unstructured data?
Format – Structured data is organized and formatted according to a predefined schema, whereas unstructured data lacks a consistent structure or format.
Storage – Structured data is typically stored in relational databases or data warehouses, while unstructured data may be stored in file systems, NoSQL databases, or data lakes.
Accessibility – Structured data is easily accessible and query able using SQL (Structured Query Language) or similar database query languages, whereas unstructured data often requires specialized tools and techniques for extraction and analysis.
Analytical Capabilities – Structured data lends itself well to traditional analytics methods such as statistical analysis and reporting, whereas unstructured data requires advanced analytics techniques such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and image recognition.
Volume – Structured data tends to be smaller in volume and more manageable, while unstructured data can be massive and grow exponentially over time.
Significance in Business
Understanding the differences between structured and unstructured data is essential for businesses looking to harness the full potential of their data assets. While structured data provides valuable insights into operational efficiency, customer behavior, and financial performance, unstructured data holds untapped potential for sentiment analysis, market trends, and customer sentiment. By integrating structured and unstructured data sources, organizations can gain a holistic view of their business landscape and drive data-driven decision-making.
Conclusion about structured and unstructured data
Structured and unstructured data represent two distinct but complementary forms of information that play a pivotal role in the digital economy. By recognizing the differences between these data types and adopting appropriate analytics strategies, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth, innovation, and competitive advantage in today’s data-driven world. Embracing both structured and unstructured data is key to staying ahead in an increasingly complex and interconnected business environment.

